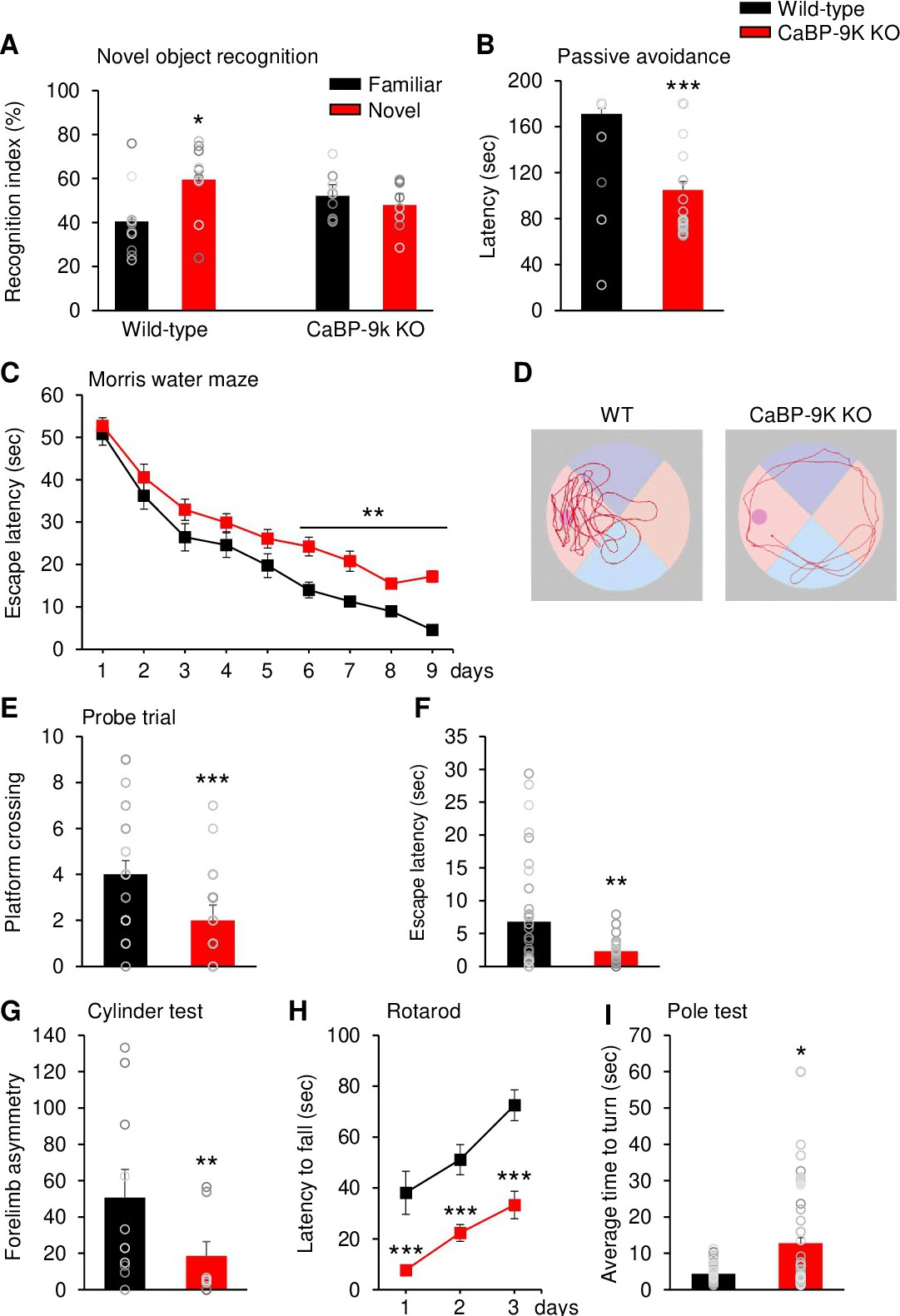
Fig. 5. CaBP-9k knockout mice show impaired memory and motor behavior. (A) Old wild-type and CaBP-9k KO mice were assessed in the novel object recognition test; the time spent exploring the objects is represented as a recognition index. n = 10 for mice for each group. (B) Old wild-type and CaBP-9k KO mice were assessed in the passive avoidance test; the latency to enter the dark compartment was recorded. n = 10 for mice for each group. (C) The Morris water maze assay reveals performance during training trials in old CaBP-9k KO and wild-type mice. (D) Representative swim paths of old mice during a probe trial after training. (E,F) Quantification of D. The old CaBP-9k KO mice exhibited decreased platform crossing numbers and escape latency. n = 12 for wild-type mice; n = 10 for CaBP-9k KO mice. (G) Contralateral forelimb use was assessed in old wild-type and CaBP-9k KO mice in the cylinder test. n = 6 for mice for each group. (H) The latency to fall was assessed in old mice in the rotarod test. n = 30 for mice for each group. (I) The turning time was assessed in old mice in the pole test. n = 10 for mice for each group. Data shown are the means ± SEMs and were analysed by two-tailed unpaired Student's t-tests.